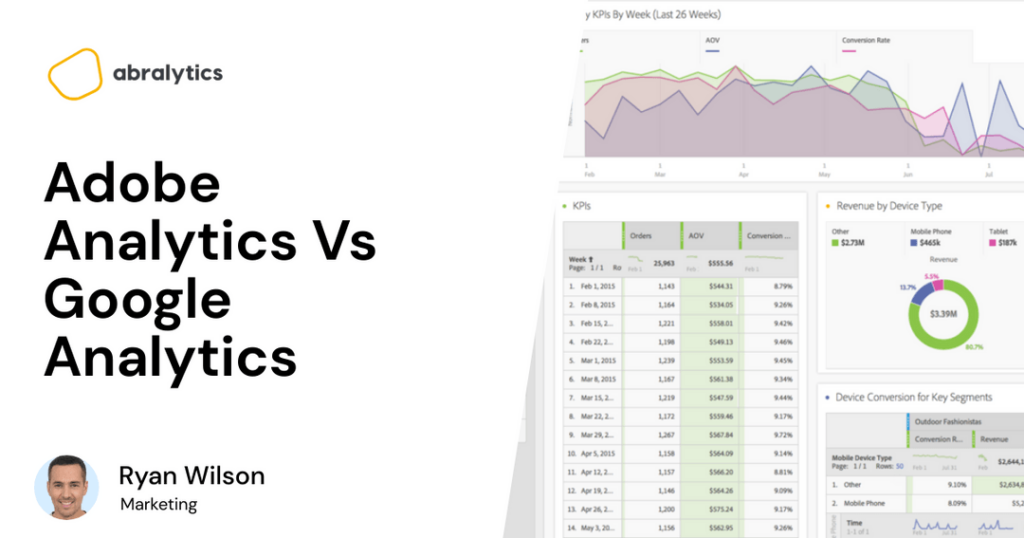
So you’ve heard that web analytics is key to the success of any website, and maybe you’ve spent some time trying out Matamo’s platform. And while Matomo is a fantastic product, perhaps you’ve realized it’s just not the right fit for you. Maybe it’s not user-friendly enough for newbies or you may be craving more advanced features that meet the specific needs of your business. We’re here to help! If you’re ready to discover the five best Matomo alternatives, read on as we discuss Matomo and its five best options; their differences, pros and cons, the best alternative for different user types and FAQs. 5 Best Matomo Alternatives 1. Abralytics At Abralytics, we love our product and will shamelessly include it as number 1 on our list – Because we believe it’s that good! Let me tell you why. Abralytics is a web analytics tool that measures, analyzes, and reports web data to optimize website usage so that you can make better data-driven decisions to achieve your business goals. As a digital marketer, Abralytics can help you see what to adjust on your marketing funnel for a better conversion rate. And you can also be sure of an analytics solution that stores data efficiently. The web tracking tool offers features such as: conversion tracking campaign and multiple site management site search referral source and time-on-site tracking form analytics keyword and goal tracking 100% data ownership user interaction and pageview tracking Matomo vs. Abralytics Matomo and Abralytics perform similar functions like data collection, storage, protection, and report generation. However, they have some features that set them apart from each other. Apart from their user interface and other features, the core differences are the pricing plans, trackable metrics, and loading speed. Pricing Plans For Matomo, you can choose between Matomo Cloud and Matomo On-Premise. Matomo Cloud: Just like Google Analytics, this version of Matomo is cloud-hosted. Matomo cloud price plan runs from $0 (free for 21 days) to $15,250. Matomo On-Premise: Matomo On-Premise in itself is FREE. But for better analytics, you can get some specific bundles at a cost. Examples of these bundles are SEO web vitals (from $86.67 per annum), multi-channel conversion attribution (from $86.67 per annum), and Roll-Up reporting (from $218.33 per annum), etc. Abralytics has three packages; Basic, standard, and Enterprise. And before you sign up, you have the option of running a 30-day free trial that allows you to test out the full range of features. Basic: $19/month – best for small businesses & early-stage start-ups Standard: $49/month – best for companies with significant traffic or web agencies Enterprise: $149+/month – best for enterprises or web agencies with large amounts of traffic Differences In Their Tracking Features Both platforms monitor metrics such as real-time users, referrers, user locations, top-performing landing pages, top exit pages, device and operating system, traffic sources, etc. But let’s take a closer look at their tracking limitations and see which of the two offers better-advanced tracking options. If you choose the Basic Matomo Cloud as your product analytics software, you can only add 30 users, 150 goals, 100 segments, 30 websites, and 30 custom dimensions. However, with Abralytics, you have Unlimited websites, 10m+ monthly events, unlimited users, email reports, data export, white-label, custom domain, and API access. Loading Speed The loading speed of a website is proportional to the size of the script. As a result, the smaller the script’s size, the faster the website is. Abralytics script weighs less than 4 KB, compared to Matomo’s 22.8 KB. This means it will load 6x faster than Matamo! So, if you desire a web analytics tool that loads with blazing speed, you should opt for Abralytics. Why Is Abralytics A Great Matomo Alternative? Source: Pexels User-friendly Interface With Abralytics, you can easily navigate its interface and dashboard to find out what’s working and what needs improvement within just two minutes of interacting with the website. Privacy Abralytics prioritizes privacy by replacing cookies with anonymous measurements. So if you’re concerned about user privacy, you need not worry because Abralytics is fully compliant with GDPR, CCPA, and PECR. Who Can Use Abralytics? In short – Everyone! From a one-person show to a vast enterprise, Abralytics is for you. Because of our pricing structure, small businesses on a tight budget won’t need to pay for unnecessary extras. While larger businesses or web agencies can choose a plan which allows them to access larger volumes of data and reports. 2. Google Analytics Source: Google Analytics Why Is Google Analytics A Great Matomo Alternative? Users’ Segmentation Google Analytics segments your website users into different groups based on their characteristics. With this, you can understand your website visitors better by zooming in on a specific area of the user metric. You can create custom segments in addition to the system segments specified by Google Analytics to make better data-driven decisions. eCommerce Conversion Tracking With Google Analytics, you can easily set up eCommerce conversion tracking. Furthermore, this shows what happens after a user interacts with your ad. Who Can Use Google Analytics? According to W3techs, about 85% of all websites use Google Analytics to track website traffic. These include top companies like YouTube, Instagram, Zoom, etc. The free version, now known as GA4, is ideal for individual users and small businesses with less website traffic, while the paid version is best for big enterprises. However, those new to analytics might find a steep learning curve because of its interface and complex dashboard. Google Analytics is ideal for those with experience because of the jargon, the sheer number of reports, and other advanced analytics features it has. For a more in-depth article on how Matamo compares with Google Analytics, click here. 3. MonsterInsights Source: MonsterInsights Dashboard Do you want a Matomo alternative for your WordPress website? MonsterInsights is a great web analytics tool for you! It allows you to track your website analytics without writing code.