Every website talks. Before data analytics, we couldn’t hear the voices of our websites. But how do you know what your website is saying? Simple – Event tracking!
Event tracking gives you a picture of how users engage with your website and business.
Do you want to know more? Then, read on as we explore everything you need to know, including what it is, why you should track events, how to manage events data, and other relevant FAQs you may have.
What Are Events In Google Analytics?
Events are specific forms of user interactions with parts of a website that you can track in Google Analytics. For example:
- Menus
- Buttons
- Videos
- Podcasts
- Gadgets
- External links
- Lightbox
- Scroll bar
- Images
- Forms, etc.

Source: Pexels
Generally, users carry out actions on a website using a mouse, keyboard, form, or frame.
So, the four types of events in Google Analytics are:
- Mouse Events
- Keyboard Events
- Form Events
- Frame Events
Meanwhile, there are two categories of Google Analytics events:
- Events that result in pageviews when they occur:
For example, a user clicks on a link to your blog (or any internal link) from your landing page.
- Events that do not result in pageviews when they occur:
Examples of this include:
- File downloads
- Watching a video
- Log-ins
- Clicking an image
- Scrolling through a web page
- Loading pop-ups, light boxes, Ajax, JavaScript, and Flash contents
What Is Google Analytics Event Tracking?
Event tracking in Google Analytics is tracking user interaction with elements of your website. Essentially, it monitors and records key user actions on your website. Google Analytics event tracking data includes:
- Total events and average events per session on your website
- Total events relating to events categories and individual events
- Session data, such as pages per session and session duration, for events and each event category
- E-commerce data like eCommerce conversion rate and average order value for events and event categories.
Examples Of Event Tracking Reports In Google Analytics
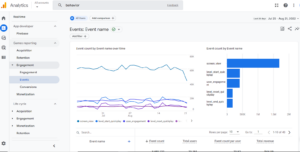 Source: Google Analytics Demo
Source: Google Analytics Demo
Event Overview Report
The Overview report compiles vital event data, such as the overall number of events, top event categories, the number of events per session, etc.
Top Event Report
You can switch between your event categories, actions, and labels in the Top Events report. This report is crucial for digging further into research on a specific event category.
Event Pages Report
The Event Pages report displays the pages where events are triggered. In this section, we can examine the top pages that drive events.
Events Flow Report
The Events Flow Report shows you the order that viewers trigger events on your website. It shows you the path they take as they move from one event to the next and helps you to determine which content engages your audience the most.
How Event Tracking Works
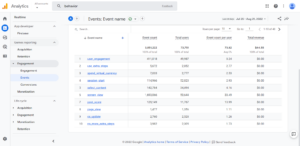 Source: GA Sample Event
Source: GA Sample Event
Events in Google Analytics have four main elements. They are also a part of the event tracking code. Google Analytics uses these codes to track user interactions and group them into event reports.
Here is how each of the four elements of event tracking affects your website:
- Events Category (mandatory): this is the title given to a group of events, such as videos, call-to-action buttons, e-commerce, etc.
- Event Action (mandatory): this is the type of user engagement you want to track, such as form button clicks, play button clicks, etc.
- Event Label (optional): this is a means to include extra details about specific website elements to define a special event, such as a product name, video title, or URL.
- Event Value (optional): refers to the process of giving an event a numerical value, such as a download time or a monetary amount.
Setting Up Event Tracking From Your Google Analytics Account With Google Tag Manager
Here is a step-by-step guide on how you can set up event tracking from your GA account so you can collect and analyze event data:
Step 1: Choose The Parameters You Want To Track In Google Tag Manager
To achieve this, carry out the following set of actions:
- Go to the dashboard of your Google Tag Manager (GTM). Then, select “Variables” > “Configure”.
- A list of the parameters you can track on your website is on the right. Under Clicks, Forms, and Videos, double-check each parameter.
- After checking all necessary fields, you can click “X” to close the window and return to the Overview menu on the left.
Step 2: Add A New Tag To Your Google Tag Manager
The next set of actions are necessary to do this:
- As your tag type, choose Google Analytics: Universal Analytics by clicking on “Add a new tag.”
- Next, change the track type to Event.
Step 3: Add A New Tag To Your Google Tag Manager
The components of the event category, action, label, and value play a role in this. By using the “+” button, you can manually fill out these fields or built-in variables.
Meanwhile, you can specify whether or not to count a session containing this interaction as a bounce by using the ‘Non-interaction hit’ parameter.
Important to note:
- If you choose “True,” GA will classify a session as a bounce when a visitor lands on a page, triggers the event (for instance, by submitting a contact form), and then leaves.
- Selecting “False” will prevent that session from being a bounce.
- If you haven’t done so, you may need to set up a variable in the Google Analytics Settings box. Click “New Variable…” if you can’t find one to choose.
After this, enter your GA tracking ID in the Tracking ID field. Then click “Save.”
Note: By selecting Admin in the bottom left corner, then Tracking Info (under Property) > Tracking Code, you can access your tracking ID in your Google Analytics account. Your ID will be on top of the screen.
Step 4: Set Up Triggering Events
To do this, follow the next series of actions:
- After configuring the fields, select the “Triggering” section.
- When configuring your new trigger, click the “+” button, then the “pencil” button, then choose your trigger type.
- Label your trigger and specify the conditions that lead to trigger firing.
- After you’ve finished configuring the trigger, click ‘Save.’ Lastly, in your event tag configuration, click ‘Save.’
Why You Should Track Event Data

Source: Pexels
Event tracking offers your product a wide range of advantages and benefits.
Not only can you monitor fundamental data-viewing indicators like page views and traffic sources, but event tracking also enables you to comprehend the drivers behind each consumer touchpoint.
Here are the reasons to track event data below:
1. Reveals Details About User Demographics
People from various countries, professions, genders, and ages make up your customer base. Event tracking reveals user behavior from different demographic groups, and this data shows the diverse interests of your customer segments.
Based on the activities done by these categories, you can tweak your marketing campaigns and ads.
2. Identify The Elements That Users Interact With
Event tracking shows which website elements consumers interact with. Metrics like pageviews, average time on page, entrances, bounce rate, and page value can be seen under Behavior > Site Content > All Pages.
For example, if you run an e-commerce business (online store) and want to see how well your white sneakers are doing.
Although the Behavior report tells you how many people visited your product page, it doesn’t show how they interacted with it. When it comes to knowing which sections and elements are guiding customers through your conversion funnel, you still won’t know.
So, without event tracking, GA reports will only count visits as single-page sessions, even if users spend a lot of time on one page and engage with it significantly (and a bounce).
3. Increase The Accuracy Of Your Site’s Bounce Rate
Event tracking provides a more accurate picture of your site’s bounce rate metric. But how does event tracking achieve this?
Single-page sessions known as bounces start and conclude on the same page. Without event tracking, GA will classify a user’s visit as a bounce if they don’t navigate to another page, regardless of how they interact with it.
For example, a video-rich page can have a higher bounce rate if events are not tracked. With event tracking, GA will only monitor bounces for visitors who didn’t watch the video, which makes more sense.
However, for GA to take event hits into account when measuring bounce rates, you must choose “Non-interaction event” as “False” during the GTM setup.
4. Set Goals And Keep Tabs On Crucial Conversions
Setting “event goals” with event action is an excellent way to keep track of user activities you value highly, such as new lead submissions or clicks on a call to action.
Besides, you can view goal reports by going to Conversions > Goals > Overview and selecting the specific event goal you wish to follow from the drop-down menu.
How To Configure Event Goals In Google Analytics
If you want to configure event goals in Google Analytics, follow the next few steps:
- Click “Admin” in the bottom right corner of the Overview report.
- Next, choose “Goals” from the View column.
- Then select “+ New Goal.”
- Go to Goal Setup and choose “Custom.”
- Name your event goal and select the ‘Event’ option under the Goal description.
- Set your event conditions in the Goal Details section.
- Lastly, select “Save” and “Done.”
Getting Relevant Insights From Event Tracking

Essentially, in the Behavior > Events > Overview report, you can track the following metrics:
- Total Event: gives you an idea of how many times events occurred.
- Unique Event: tells you the number of times an event occurred at least once during a session.
- Event Value: product of the total events and values assigned to each.
- Average Event Value: ratio of the total value of each event to the number of events.
- Session with Event: provides insight into how many sessions at least one event is triggered.
- Events/ Session with Event: informs you about a session’s overall number of events.
But this overview doesn’t provide actionable insights; it’s just a broad overview of what happened on your website without any context or specifics regarding user behavior.
Meanwhile, the Behavior > Events > Top Events report can offer more relevant information, such as:
- How do particular website interactions affect your e-commerce metrics?
- How a specific event affects user behavior with a product.
- Segment your insights by including secondary dimensions like source/medium, device category, landing page, and user type.
Common Event Tracking Use Cases
Here are the most common event-tracking use cases:
- Consent Interactions: How many users reject cookies for advanced marketing?
- Page Interactions: Are visitors clicking on the flashy tabbed content on your web page? Or that lightbox for images?
- File Downloads: How many users downloaded PDF brochures?
- Ecommerce Interactions: Do visitors add your products to their carts but then abandon them?
- Social Media Button Interactions: How many visitors use your site to find your social media profiles? Do they click those buttons on your blog posts to share content?
- Form Events: Are your forms having any problems? Do people begin them but then never submit them? But you might also want to think about Form Analytics.
- Lead Generation: Which pages have the most sign-ups for your newsletter?
- Non-Page Links: How many site visitors click the email and phone links?
- Screen Interactions: Are website visitors scrolling down far enough to see the footer?
Events are ideal for setting up Goal Conversions since they offer a high-level picture of how visitors use your website.
For instance, if you want website visitors to fill out a form for a newsletter subscription.
Events tracking lets you track how many users start and complete each form on your website. Meanwhile, goals will show how many site visitors used your newsletter subscription form to become leads. So you can track the entire user journey by combining them with the Funnels feature.
Final Verdict
Event tracking is crucial to your website analytics. It lets you monitor user interactions with elements of your site.
As a digital marketer, event tracking can help you achieve better results from your marketing campaigns by helping you track how users engage with your content. With this, you can see what to tweak for better conversion rates.
If you found this article helpful, check out similar articles on Abralytics, a google analytics alternative.
Other related articles
- How Website Performance Affects Conversion
- How To Measure How Long Someone Stays On A Website
- How To Measure Website Traffic
- How to delete goals in Google Analytics
You might be interested in this article: